Exploring carbapenem resistance with CRISPRi
Carbapenems are antibiotics reserved for the most severe multidrug-resistant. At PlasmidLab, we study one of the key players in hospital-acquired carbapenem resistance: the plasmid pOXA-48. Our goal was simple but ambitious: to uncover the role of each of its genes by switching them off one at a time.
Scanning a complete genetic map
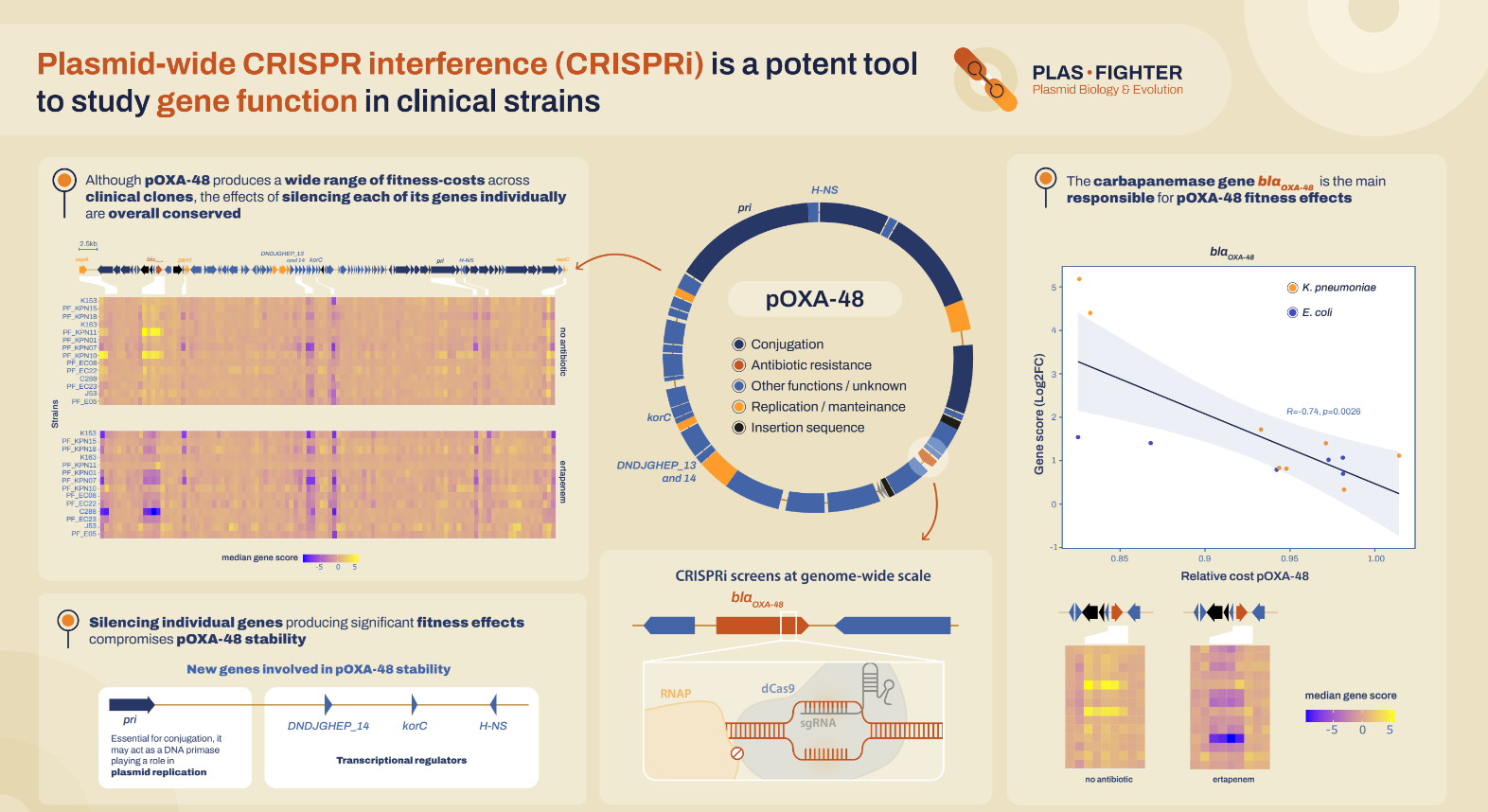
We designed a tool called CRISPR interference capable of precisely silencing any region of pOXA-48. With it, we were able to target each gene and intergenic region of the plasmid individually and observe their impact on the bacterial host. And we did so across 13 clinical Enterobacterales isolates collected in hospitals—something that had never been attempted before.
Into the pOXA-48 plasmid
Silencing genes is a powerful way to understand how each one contributes to the plasmid’s stability—and to the bacteria. In the case of our protagonist, pOXA-48, we observed that the function of each gene remained consistent between strains, although the overall effect of carrying the plasmid varied across them.
We identify some genes as true structural pillars: repA, pri, and the PemI/PemK toxin–antitoxin system, which prevents the plasmid from being lost when the bacterium divides.
But the most striking finding was about the blaOXA-48 gene, already known to enable resistance to carbapenems. In every strain, this gene consistently imposed the bacterium’s fitness cost. In other words, it was the main reason why carrying the plasmid slowed bacterial growth. When we turned blaOXA-48 off, the bacteria grew better and faster… but in doing so, they lost their resistance.
Understanding AMR brings us closer to solving it
This study sheds new light on one of the most critical resistance mechanisms threatening global health. By identifying which parts of pOXA-48 are essential for its maintenance and which ones drive bacteria’s stability and resistance potential, we open the door to more refined strategies to combat antimicrobial resistance.
Our work in various formats
We’ve turned our study into an infographic where you can explore the figures corresponding to the key results of our work. Download it to see the findings at a glance!
